General Health Care for Pet Ferrets
Health tips and advice for your ferret friends.
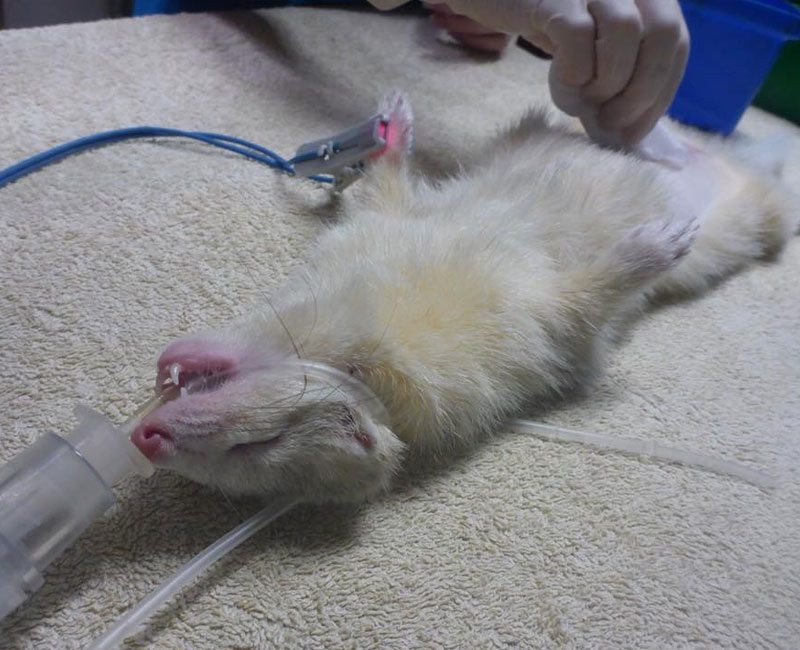
Female Ferret Sterilisation
Reasons For Sterilising Your Female Ferret

Prevent fatal estrogen toxicity
Prevent pregnancy

Prevent uterine and ovarian disease and tumours
The Procedure
Your ferret will get an intramuscular sedation that will make her fall asleep in 5 to 10 minutes. We then prepare the area on the ventral abdomen for surgery. She will then be placed on anaesthesia for the duration of the surgery. A two centimetre incision is made just behind the belly button and the uterus and ovaries are removed. The abdominal muscle and skin is closed with absorbable sutures. The sutures are hidden underneath the skin so your ferret won’t be able to pull them out. There is no need to remove any stitches later on.

Male Ferret Castration
Castration should be done by 6-8 months of age. Reducing the odour produced by the sebaceous glands on the skin is one of the main reasons owners get their ferrets castrated.
Reasons For Sterilising Your Male Ferret

Reduce body odour

Prevent testicular neoplasia and prostate problems

Prevent aggression

Parasites
Canine distemper virus is a fatal disease in ferrets and is a significant risk and the disease is ubiquitous. It is a prevalent disease in dogs and transmission of the virus is most commonly accomplished by aerosol exposure. Direct contact with conjunctival and nasal exudates, urine, faeces and skin also cause infection.

No treatment is available and mortality is 100% in ferrets

Vaccination is done at: 6 weeks, 10 weeks and 14 weeks

Revaccinate yearly
Parasite Prevention
Gastrointestinal parasites are uncommon in ferrets compared to cats and dogs. Rarely can they get infected with nematodes from other natural hosts. Giardiasis is occasionally seen in ferrets and occurs after exposure to infected dogs and cats in pet stores. Ear mites are very common in ferrets but affected animals rarely show pruritus or irritation from infestation.
Heartworm can cause disease in ferrets. Ferrets that are housed outdoors in heartworm-endemic areas are most susceptible to infection. All ferrets in endemic areas should be given preventative medicine.
Flea infestation is most common in ferrets kept in households with dogs and cats, and affected ferrets can become severely anaemic from chronic infestations. Advocate cats<4kg can be used in ferrets to control fleas and heartworm.
https://www.advocate-spot-on.com/en/for-ferrets/how-to-apply
Advantage top spot can be used if you only want to control fleas.

Ferret Husbandry
Nutrition
Ferrets are strict carnivores that depend on meat protein and fats for their dietary requirement. The protein in the diet should be of high quality and easily digestible because of the ferret’s very short intestinal transient time of 3-4 hours. It is not recommended to feed a diet rich in carbohydrates as they do not have the flora to digest it. Due to the high metabolic rate a dry ration is preferred over a canned product. We recommend a high-quality dry kitten food or ferrets food and for added fat use commercial available fatty acids.
Housing
Ferrets can be trained to use the litterbox relatively easily. However, because of their short digestive transit time, they might not always make it back to the cage to use the litterbox. Having several litterboxes around the house is a good idea.
Bathing
Ferrets, like cats, do not require routine bathing. Intact ferrets of both sexes develop a very strong body odour during the breeding season. Frequent bathing may strip the skin of essential oils and produce a pruritic condition. We recommend to bath using cat or ferrets shampoo no more frequently than once a month.
Call our team for any further information about caring for your pet ferrets. We’ll be happy to help!
Ferret owners from all over Fremantle, Hilton, Hamilton Hill, O’Connor, White Gum Valley, Beaconsfield, Willagee, Samson, Coolbellup, Kardinya, Spearwood and Coogee have been coming to Hilton Vet Hospital for more than 30 years to receive exceptional service and care for their pets.
